In robotics, an end effector (or end-of-arm tooling) is the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment. The exact nature of this device depends on the application of the robot. In the strict definition, which originates from serial robotic manipulators, the end effector means the last link (or end) of the robot. The most essential robot periferial is the end effector, or end-of-arm-tooling (EOT). There are very different application for EOT. EOT are frequently highly complex. They can carry out different activities at the same time and may utilize various sensors.
End effector types
-
- Mechanical gripper- two or more fingers that can be actuated by a robot controller to open and close on a workpiece
- Vacuum gripper- suction cups are used to hold flat objects
- Magnetised device- making use of the principles of magnetism
- Adhesive device- deploying adhesive substances these hold flexible materials, such as fabric
- Mechanical devices- simple devices, as hooks, scoops
The gripper of a bending robot is generally constructed by mounting multiple suckers on a metal frame.
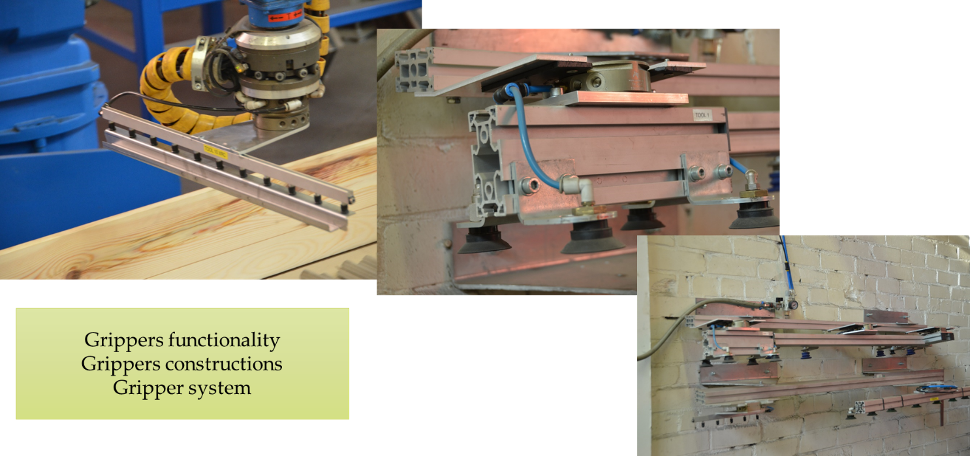
Gripper system for robot bending
Depending the tasks in the robot-cell (workpieces nomenclature, weight of plates, measures of workpieces) the construction and functionality of end-effector is determined.
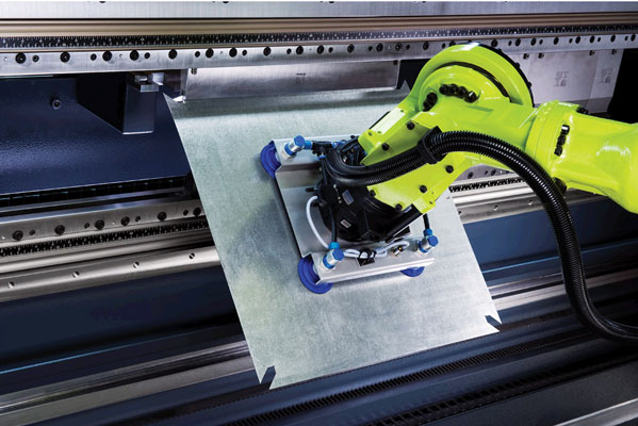

Bending gripper
Questions Q5
-
-
- What is the function of the stamp and die when bending
- What are the different bending methods. On the basis of which the choice is made
- What determines the cross-sectional shape of the stamp. Give examples
- What is meant by air bending and minting
- What is the relationship between the bending angle and the required bending force
-
Tasks T4
-
-
- How to calculate the page area based on a drawing of the final product
- Based on the product to be manufactured, solve the problem of product bending (what issues need to be solved in the workplace)
-
- Assuming that the company does not yet have a bending job
- Assuming that there is a robot bending job in the company
- Assuming they are previously manufactured products
-
-
- Design a robotic bending workstation to fabricate a given product and create a bending cycle and determine the approximate time required to bend the product.
- Select the bending tools and robot gripper to make this product in the robotic workplace
- Compare the cost of manufacturing the product for robotic bending and conventional bending. Find the payback period and determine the risks with robot bending
-
