An Industrial Robot is defined by ISO 8373 as an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator, programmable in three or more axes.
| Robot producers | Installed worldwide |
| ABB | 300.000 |
| The Yaskawa Electric Corporation | 360.000 |
| Midea Group (KUKA) | 80.000 |
| The Fanuc Corporation | 400.000 |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | 110.000 |
| Epson Robotics | 55.000 |
| Stäubli Robotics | 45.000 |
| Nachi Fujikoshi Corporation | 100.000 |
| Denso Robotics | 95.000 |
| Comau | 30.000 |
| Omron Adept | 25.000 |
| Mitsubishi Robotics | 70.000 |
| Fox Conn | 40.000 |
| Universal Robotics | 20.000 |
| Doosan Robotics | |
| Techman Robotics | |
| Rethink Robotics | |
| Bosch |
To find the producers of industrial robots
- www.abb.com
- www.fanucrobotics.de
- www.kuka.com
- www.staubli.com
- www.mitsubishi.com
- www.scara-robots.com
- www.motoman.com/products/robots
- http://www.allonrobots.com
References
[1] ISO 8373:2012 Robots and robot devices. Vocabulary.
[2] Robotics Industries Association (RIA) [ www.robotics.org ]
[3] Industrial Robots [ https://ifr.org/img/office/Industrial_Robots.2016.Chapter_1_2.pdf
Industrial robots application areas
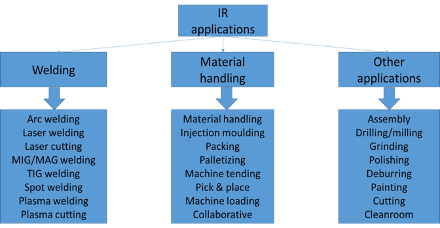
Figure 1.1. Industrial robots application areas
Industrial robot classification – basic parameters description in the selection process
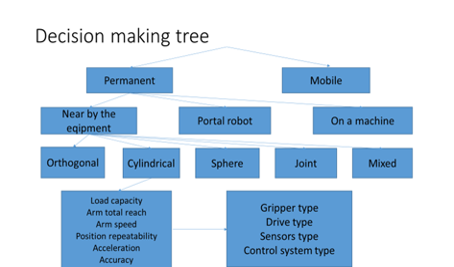
Figure 1.2 Classification of industrial robots
Industrial robots classification
ISO has outpointed also some significant criteria for robot classification:
According to main actuating power source:
-
- pneumatic,
- hydraulic,
- electric.
According to the type of motion control:
-
- point-to-point,
- continuous trajectory control.
- According to the programming models:
- through direct learning,
- trajectory generation,
- off-line.
According to the types of sensors employed:
-
- position detecting units,
- simple linear logic,
- sensors for signal proportional to the deviation.
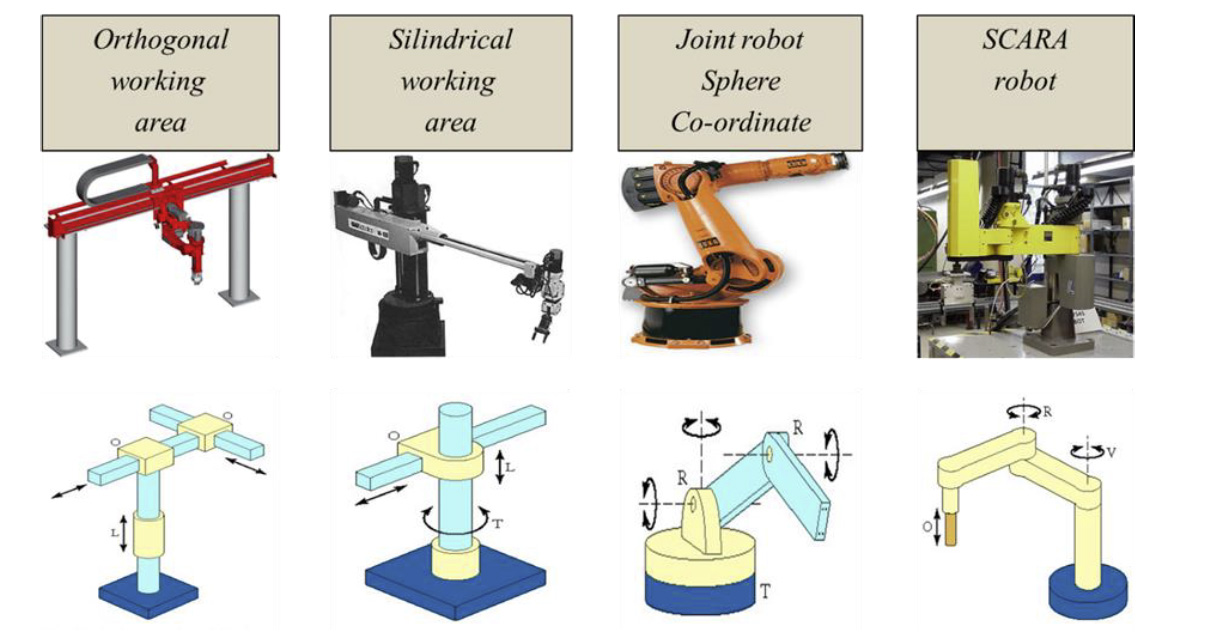
Figure 1.3. Basic types of industrial robots
The basic features of industrial robots are described with certain parameters which are forming their technological capabilities. In the table 1 are given the importance or how necessary is to consider (weakly, on average, strongly) these features on the case of area of using the industrial robot.
Table 1.1 The technological capabilities of IR in different application areas
| Technological capabilities
|
Material
handling |
Machining | Welding | Assembly | Painting |
| Degree of freedom
|
Weakly | Strongly | Strongly | Strongly | On-average |
| Positioning accuracy
|
On-average | Strongly | Strongly | Strongly | On-average |
| Motion speed
|
On-average | Strongly | On-average | Strongly | On-average |
| H-reach
|
Strongly | On-average | On-average | Weakly | Strongly |
| Payload
|
Strongly | Weakly | On-average | Weakly | Weakly |
| The need of use of sensors
|
Weakly
|
Strongly | Strongly | Strongly | On-average |
| The need of different end- effectors | Weakly | Strongly | Weakly | Strongly | Weakly |
Table 1.2. Industrial robot types
| Robot types | Mechanical structure | Description | Technical parameters |
| Cartesian | 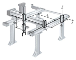 |
Cartesian robots are also called rectilinear or gantry robots and have a rectangular configuration. These types of industrial robots have three prismatic joints to deliver linear motion by sliding on its three perpendicular axes (X, Y and Z). | 3-axis |
| Cylindrical | 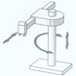 |
Cylindrical robots have at least one rotary joint at the base and at least one prismatic joint connecting the links. These robots have a cylindrical workspace with a pivoting shaft and an extendable arm which moves vertically and by sliding. | 4-axis |
| SCARA |  |
SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robots have a donut shaped work envelope and consist of two parallel joints that provide compliance in one selected plane. The rotary shafts are positioned vertically, and the end effector attached to the arm moves horizontally. The SCARA robots can move faster and have easier integration than cylindrical and cartesian robots. | 4-axis |
| Articulated |  |
Articulated robots are one of the most common types of industrial robots. It resembles a human arm in its mechanical configuration. The arm is connected to the base with a twisting joint. The number of rotary joints connecting the links in the arm can range from two joints to ten joints and each joint provides an additional degree of freedom. | 6-axis |
| Delta | 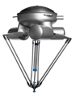 |
Delta robots are also called parallel link robots as it consists of parallel joint linkages connected with a common base. Owing to direct control of each joint over the end effector, the positioning of the end effector can be controlled easily with its arms resulting in high speed operation. Delta robots have a dome shaped work envelope. | 3-axis |
QUESTIONS Q1 – BASIC ABOUT INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
-
- What is an industrial robot (IR)
- What are the main types of IR
- What are the basic features of (IR) – see classification principles
- Why do we need the classification of IR (see Fig. 1.2)
- Describe the construction of IR (see Fig 1.3)
- How the construction of IR helps the robot to fulfil the task
- What features play the important role in different industrial tasks – bring examples (see Table. 1.1)
- Look the robots of different producers. What are the similarities and differences
- Take one application area (like welding, assembly, painting, etc) and compare the IR of different producers. Make a conclusion (see Fig. 1.1)
- Describe one IR according to the classification tree (see Figure 1.2)
TEST Statistics {0,5,10} Max = 100 {1: 0-20; 2: 21-40; 3: 41-60; 4: 61-80; 5: 51-100}
